class iii malocclusion definition
Its prevalence varies greatly among and within different races ethnic groups and geographic regions studied. National Library of Medicine 000 0 votes Rate this definition.
Pseudo dentoalveolar and skeletal.
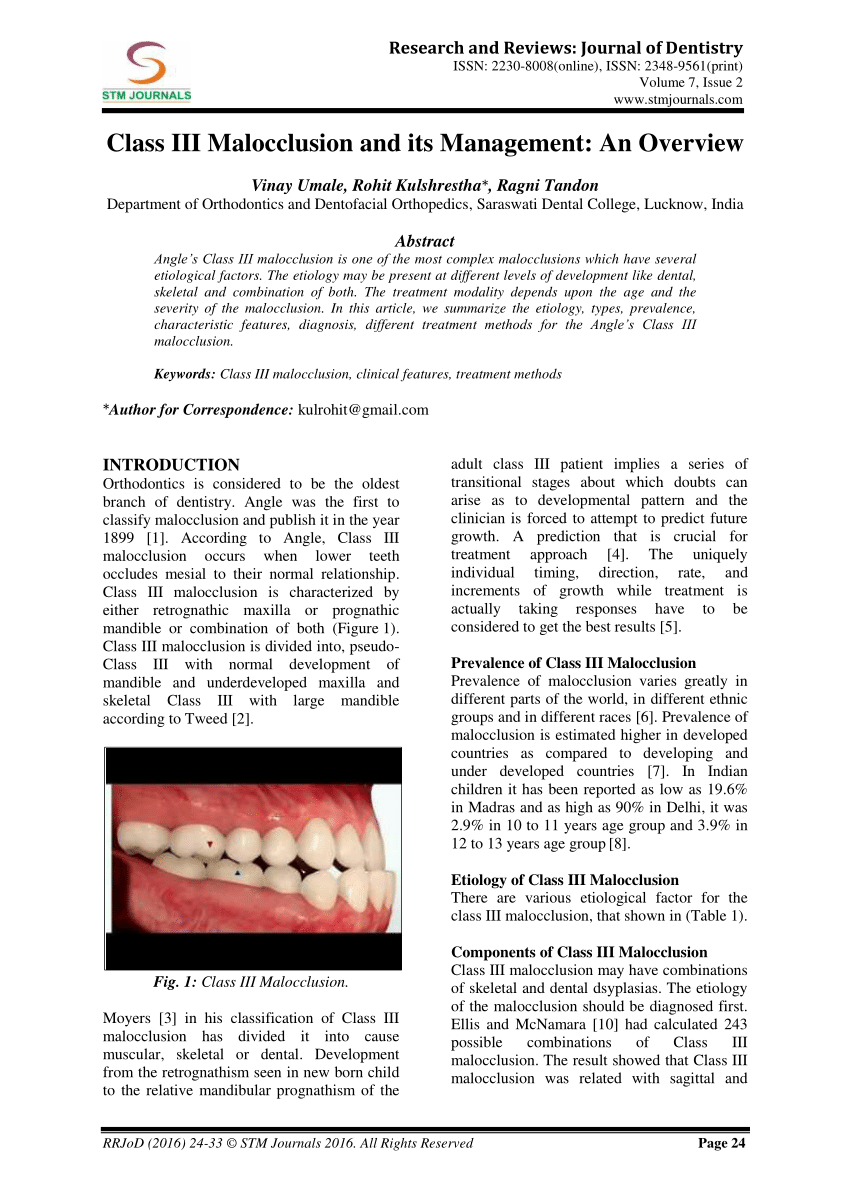
. Angle Class III malocclusions in 120 subjects who had orthognathic surgery were analyzed with cephalometrics and facial photos and classified into 3 categories based on the abnormalities of the maxilla. Contrary to class 2 class 3 malocclusions are characterized by lower molars. A severe Class III malocclusion may be associated with distortion or interdentalization lisping of sibilant and alveolar speech sounds s z t d n l due to difficulty elevating the tongue tip to the alveolar ridge.
Patients can develop a class III malocclusion for a number of. Malocclusion Severity Assessment and commented Full cusp class III will likely require extractions status of 3 is uncertain- exhibits clinical sign of ankylosis The treating orthodontist scored 2326 22 and 27 as crowded tooth 3 as rotated open space between 8. Class III malocclusion is considered to be one of the most difficult and complex orthodontic problems to treat.
Dental malocclusions are classified based on the positioning of the upper and lower molars. Class 3 malocclusion called prognathism or underbite occurs when the lower jaw protrudes or juts forward causing the lower jaw and teeth to overlap. In this article find out about class 3 malocclusion and the types of treatments that can be used to correct it.
The sound most likely to be affected is s. Prevalence of class III malocclusion in Caucasians ranges from 08 to 40 and rises up to 1213 in Chinese and Japanese populations while in North Indian population class III malocclusion is found in up to 34 of the population 1 3. 23 In adults.
This type is usually caused by a large. DRAnwar al-abbadi DRRania al-smadi DRhanan habarneh 2. 1 However dentoalveolar compensations reducing overjet and the severity of the Class II malocclusion are still the major effect of functional appliances.
Clinicians have been trying to identify the best timing to intercept a Class III malocclusion that develops as early. 1 The reported incidence of this malocclusion ranges between 1 to 19 with the lowest among the Caucasian populations 23 and the highest among the Asian populations. Ideally treatment of Class II malocclusions should focus first on improving the skeletal discrepancy using functional appliances while the individual is still growing.
Most malocclusion studies to date have focused on Class III malocclusions. TRUE class III malocclusion SKELETAL which is genetic in origin due to excessively large mandible or smaller than normal maxilla. Class 3 malocclusion is diagnosed when you have a severe underbite.
PSEUDO Class III malocclusion FALSE or postural which occurs when mandible shifts anteriorly during final stages of closure due to premature contact of incisors or the canines. A class III malocclusion is a misalignment of the teeth that results in a situation where the lower teeth are more prominent than the teeth in the upper jaw. Class III malocclusions are the least common type of malocclusion yet they are often more complicated to treat and more likely to require orthognathic surgery for optimal correction.
Class III malocclusion has 2 subdivisions. Type A is true mandibular prognathism which means that the maxilla is normal but the mandible is overgrown. An example of hereditary mandibular prognathism can be seen amongst the Hapsburg Royal family where one third of the affected individuals with severe class III malocclusion had one parent with a similar.
Class 1 dental malocclusion is the most common type of malocclusion. Class III malocclusion represents a growth-related dentofacial deformity with mandibular prognathism in relation to the maxilla andor cranial base. Class 3 is the rarest type of malocclusion.
Genetic studies for Class II and Class I malocclusion are more rare. -Class III incisor. Dental malocclusions are classified based on the positioning of the upper and lower molars.
Class 3 malocclusion 1. ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF CLASS III BY DR. Approximately 50 to 55 of children between the ages of 6 and 17 have some form of Class 1 malocclusion.
Malocclusion Angle Class III. Class 3 Malocclusion Mesiocclusion Also known as prognathism this class of malocclusion occurs when the lower front teeth are more prominent than the upper front teeth and the patient has a large lower jaw or a short upper one. Definition of a class 3 malocclusion.
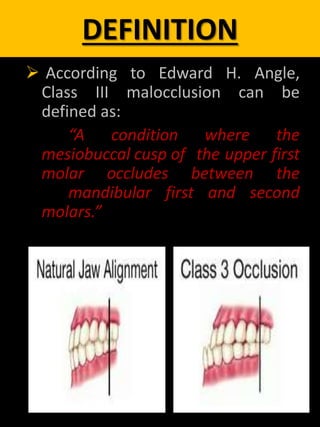
Since the 18th century this malocclusion has long been viewed as one of the most severe facial deformity. The different definitions of Class III malocclusion have been analyzed. DEFINITION According to Edward H.
Class III Malocclusion Anterior Tooth Positions Overjet is a term used to describe the distance between the. Evolution of Class III treatment in orthodontics Peter Ngana and Won Moonb Morgantown WVa and Los Angeles Calif Angle Tweed and Moyers classified Class III malocclusions into 3 types. To achieve the inclination of the upper incisors many different alternatives have been proposed such as inter-proximal reduction extractions or distalization of upper molars which has not been widely reported in the literature as a means to decompensate Class III.
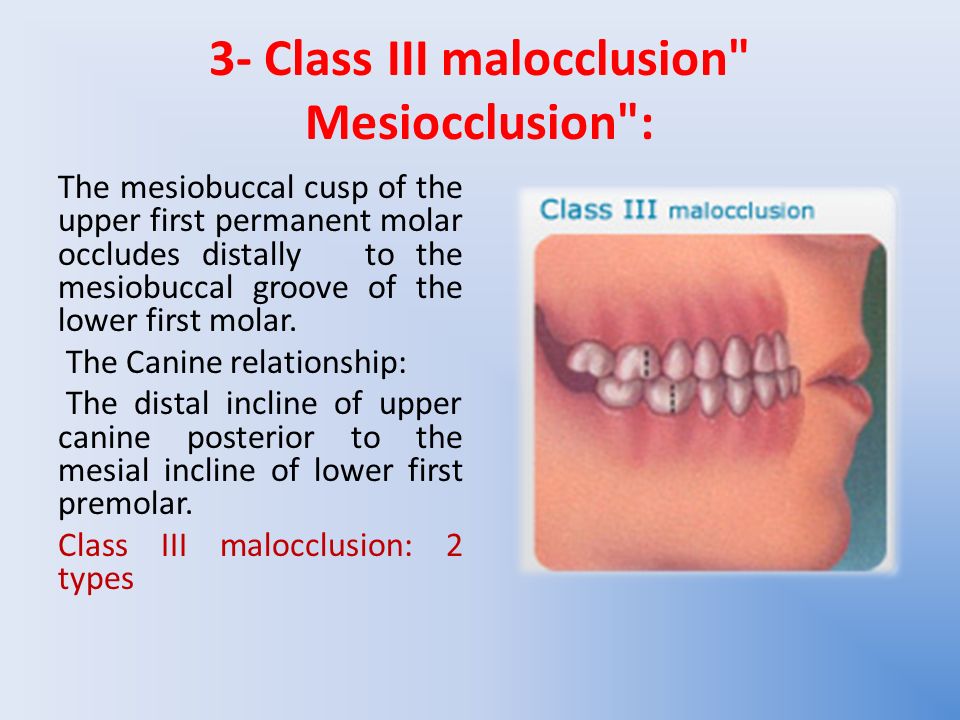
In this type of malocclusion your lower teeth overlap with your upper teeth. This condition is also known as an underbite and it is much less common than other types of malocclusions where the upper teeth are more prominent. Malocclusion in which the mandible is anterior to the maxilla as reflected by the first relationship of the first permanent molar mesioclusion.
Angle Class III malocclusion can be defined as. TASNEEM AL-RBAIHAT SUPERVISED BY. Definition of a class 1 malocclusion.
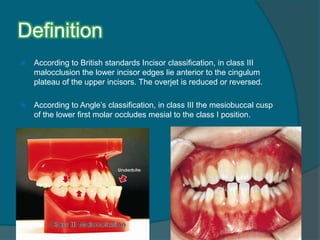
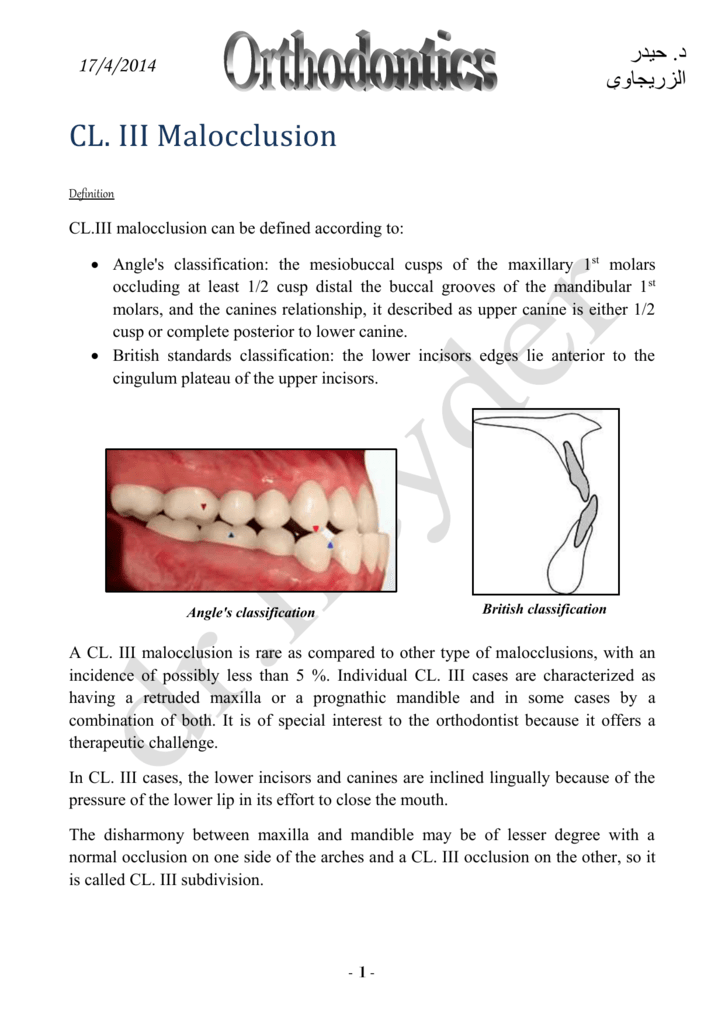
FEATURES OF CLASS III MALOCCLUSION The patient has a Class III molar relationship. A condition where the mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first molar occludes between the mandibular first and second molars 5. Is when the lower incisor edge lies anterior to the cingulum plateau of the upper incisors.
A class 1 malocclusion means that the. Class III Malocclusion A malocclusion where the molar relationship shows the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar mesially positioned to the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar when the teeth are in occlusion.
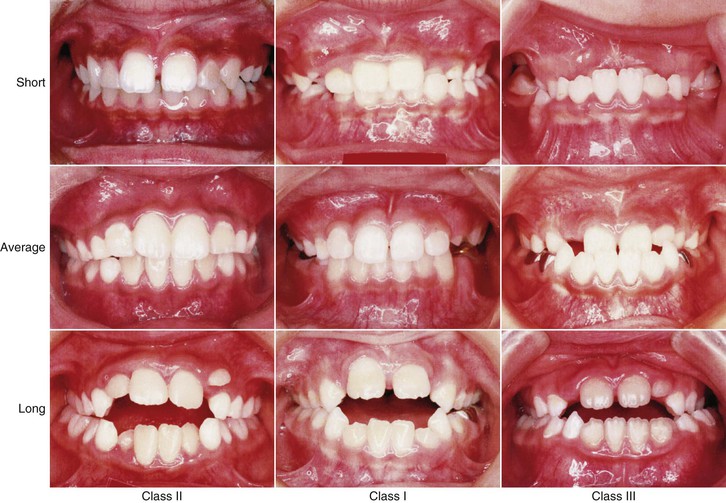
15 Clinical Practice Guidelines For Developing Class Iii Malocclusion Pocket Dentistry

Class Iii Malocclusion Vineeth Dental Implant Courses By Indian Dental Academy By Indiandentalacademy Issuu

Types Of Malocclusion And Correction Winchester Dental

Class Iii Malocclusion Ppt Download

References In Severe Skeletal Class Iii Malocclusion Treated With 2 Stage Orthognathic Surgery With A Mandibular Step Osteotomy American Journal Of Orthodontics And Dentofacial Orthopedics
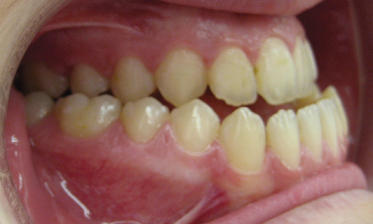
16 Class Iii Malocclusion The Evidence On Diagnosis And Treatment Pocket Dentistry

Angle S Classification For Malocclusions Dentalnotebook
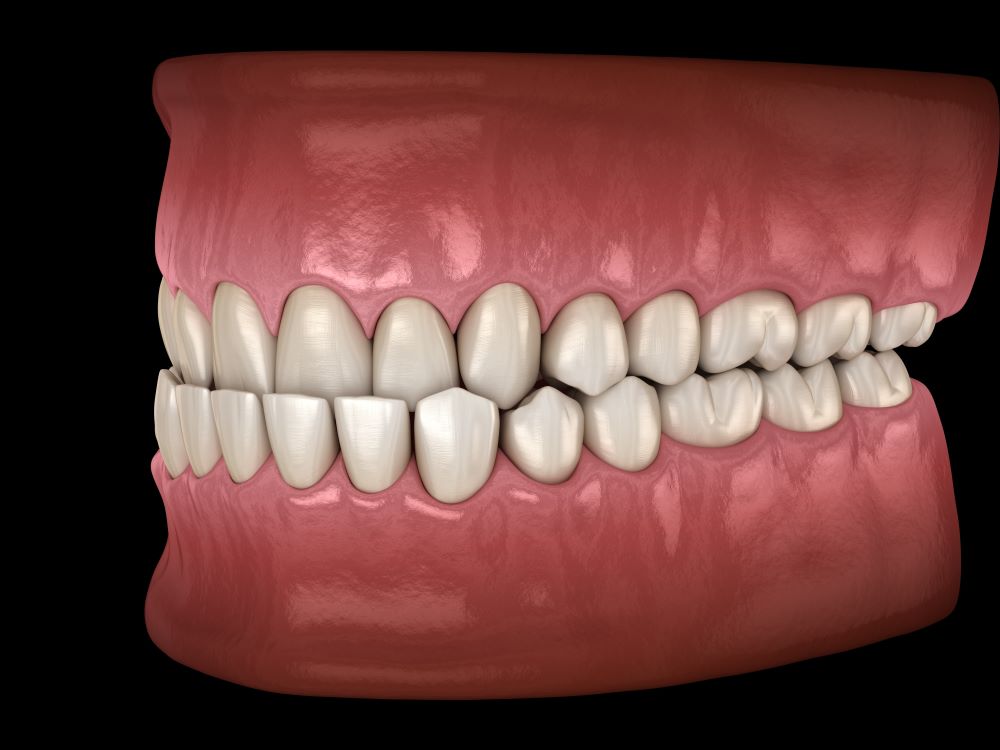
What Is A Class 3 Malocclusion Dental Information
Orthodontic Dr Enas Talb 4th Class Ppt Video Online Download

Therapeutic Management Of A Pseudo Class Iii Malocclusion Case Report Revista Mexicana De Ortodoncia

Class Iii Malocclusion Ppt Download
Treatment Of Dentoalveolar Functional Cl Iii Malocclusion

Pdf Research And Reviews Journal Of Dentistry Class Iii Malocclusion And Its Management An Overview